No. 27/153/DKom
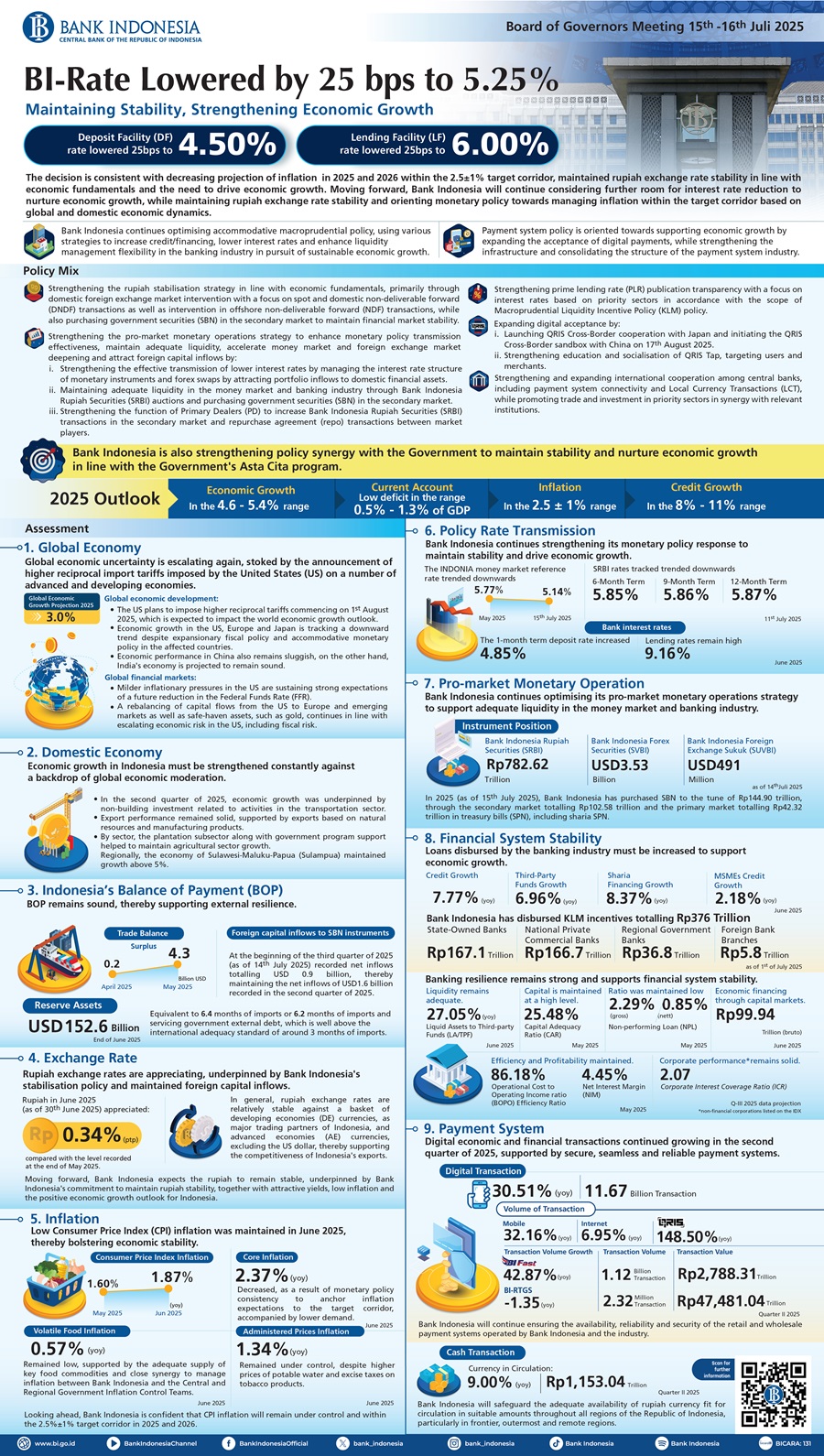
The Bank Indonesia Board of Governors decided on 15-16th July 2025 to lower the BI-Rate by 25 bps to 5.25%, while also lowering the Deposit Facility (DF) rate by 25 bps to 4.50% and the Lending Facility (LF) rate by 25 bps to 6.00%. The decision is consistent with decreasing projection of inflation in 2025 and 2026 within the 2.5±1% target corridor, maintained rupiah exchange rate stability in line with economic fundamentals and the need to drive economic growth. Moving forward, Bank Indonesia will continue considering further room for interest rate reduction to nurture economic growth, while maintaining rupiah exchange rate stability and orienting monetary policy towards managing inflation within the target corridor based on global and domestic economic dynamics. Meanwhile, Bank Indonesia continues optimising accommodative macroprudential policy, using various strategies to increase credit/financing, lower interest rates and enhance liquidity management flexibility in the banking industry in pursuit of sustainable economic growth. Payment system policy is also oriented towards supporting economic growth by expanding the acceptance of digital payments, while strengthening the infrastructure and consolidating the structure of the payment system industry.
Bank Indonesia has, therefore, strengthened its monetary, macroprudential and payment system policy mix to maintain stability in order to strengthen sustainable economic growth through the following policy measures:
- Strengthening the rupiah stabilisation strategy in line with economic fundamentals, primarily through domestic foreign exchange market intervention with a focus on spot and domestic non-deliverable forward (DNDF) transactions as well as intervention in offshore non-deliverable forward (NDF) transactions, while also purchasing government securities (SBN) in the secondary market to maintain financial market stability.
- Strengthening the pro-market monetary operations strategy to enhance monetary policy transmission effectiveness, maintain adequate liquidity, accelerate money market and foreign exchange market deepening and attract foreign capital inflows by:
- strengthening the effective transmission of lower interest rates by managing the interest rate structure of monetary instruments and forex swaps by attracting portfolio inflows to domestic financial assets,
- maintaining adequate liquidity in the money market and banking industry through Bank Indonesia Rupiah Securities (SRBI) auctions and purchasing government securities (SBN) in the secondary market, and
- strengthening the function of Primary Dealers (PD) to increase Bank Indonesia Rupiah Securities (SRBI) transactions in the secondary market and repurchase agreement (repo) transactions between market players.
- Strengthening prime lending rate (PLR) publication transparency with a focus on interest rates based on priority sectors in accordance with the scope of Macroprudential Liquidity Incentive Policy (KLM) policy (Appendix).
- Expanding digital acceptance by: (i) launching QRIS Cross-Border cooperation with Japan and initiating the QRIS Cross-Border sandbox with China on 17th August 2025, and (ii) strengthening education and socialisation of QRIS Tap, targeting users and merchants, and
- Strengthening and expanding international cooperation among central banks, including payment system connectivity and Local Currency Transactions (LCT), while promoting trade and investment in priority sectors in synergy with relevant institutions.
Bank Indonesia is also strengthening policy synergy with the Government to maintain stability and nurture economic growth in line with the Government's Asta Cita program. In addition, Bank Indonesia will continue strengthening policy synergy with the Financial System Stability Committee (KSSK) to maintain the stability of the financial system.
Global economic uncertainty is escalating again, stoked by the announcement of higher reciprocal import tariffs imposed by the United States (US) on a number of advanced and developing economies. The US plans to impose higher reciprocal tariffs commencing on 1st August 2025, which is expected to impact the world economic growth outlook, particularly in advanced economies. Economic growth in the US, Europe and Japan is tracking a downward trend despite expansionary fiscal policy and accommodative monetary policy in the affected countries. Economic performance in China also remains sluggish amid various export diversification strategies. On the other hand, India's economy is projected to remain sound on the back of domestic demand. Bank Indonesia projects flat global economic growth in 2025 at approximately 3.0%. Milder inflationary pressures in the US are sustaining strong expectations of a future reduction in the Federal Funds Rate (FFR). Meanwhile, a rebalancing of capital flows from the US to Europe and emerging markets as well as safe-haven assets, such as gold, continues in line with escalating economic risk in the US, including fiscal risk. Such developments have continued pressuring the DXY Index and ADXY Index. Moving forward, greater vigilance as well as a stronger policy response and coordination are required to mitigate persistently high global economic and financial market uncertainty, while maintaining external resilience, economic stability and sustainable growth at home.
Economic growth in Indonesia must be strengthened constantly against a backdrop of global economic moderation. In the second quarter of 2025, economic growth was underpinned by non-building investment related to activities in the transportation sector. Export performance remained solid, supported by exports based on natural resources and manufacturing products. Meanwhile, household consumption must be strengthened further, as reflected by slower retail sales growth. By sector, the plantation subsector along with government program support helped to maintain agricultural sector growth, while the performance of several other key sectors, including the manufacturing industry as well as accommodation and food service activities, remains soft. Regionally, the economy of Sulawesi-Maluku-Papua (Sulampua) maintained growth above 5%, with growth in other regions thus far failing to increase. Moving forward, national economic growth in the second semester of 2025 is projected to improve, with Bank Indonesia forecasting 4.6-5.4% growth overall in 2025. In addition to stronger domestic demand, the improvements will also stem from positive export performance as a result of tariff negotiations with the US Administration. The strong policy mix response of the Government and Bank Indonesia has bolstered economic confidence and, ultimately, boosted economic activity. In this regard, the Government has introduced fiscal stimuli in the form of social protection and the implementation of flagship programs under the auspices of Asta Cita. In addition to maintaining stability, Bank Indonesia has also oriented policy towards nurturing sustainable economic growth by lowering the BI-Rate, increasing liquidity and strengthening macroprudential incentives for the banking industry to revive lending/financing to priority sectors. Furthermore, Bank Indonesia will continue strengthening its monetary, macroprudential and payment system policy mix in close synergy with the fiscal and real sector policies of the Government in pursuit of economic growth.
Indonesia's Balance of Payments (BOP) remains sound, thereby supporting external resilience. In May 2025, the trade balance amassed a USD4.3 billion surplus, increasing from a USD0.2 billion surplus in April 2025. The positive trade balance is supported by exports of electrical machinery as well as iron and steel. Furthermore, export performance is expected to remain positive as a result of tariff negotiations with the US Administration. Meanwhile, portfolio investment inflows have also been maintained in line with the promising domestic economic outlook for Indonesia, high yields on domestic financial instruments and the rebalancing of capital flows to developing economies, including Indonesia, as economic risk intensifies in the US. Foreign capital inflows to SBN instruments at the beginning of the third quarter of 2025 (as of 14th July 2025) recorded net inflows totalling USD 0.9 billion, thereby maintaining the net inflows of USD1.6 billion recorded in the second quarter of 2025. The position of foreign reserves at the end of June 2025 remained high at USD152.6 billion, equivalent to 6.4 months of imports or 6.2 months of imports and servicing government external debt, which is well above the international adequacy standard of around 3 months of imports. In 2025, Bank Indonesia projects 2025 BOP to record a lower current account deficit in the range of 0.5% to 1.3% of GDP range, accompanied by a maintained capital and financial account surplus despite persistently high global uncertainty.
Rupiah exchange rates are appreciating, underpinned by Bank Indonesia's stabilisation policy and maintained foreign capital inflows. The value of the rupiah in June 2025 (as of 30th June 2025) appreciated by 0.34% (ptp) compared with the level recorded at the end of May 2025. The latest developments in the middle of July 2025 (as of 15th July 2025) indicate rupiah stability despite increasing global uncertainty. In general, rupiah exchange rates are relatively stable against a basket of developing economies (DE) currencies, as major trading partners of Indonesia, and advanced economies (AE) currencies, excluding the US dollar, thereby supporting the competitiveness of Indonesia's exports. Exchange rate performance is supported by consistent stabilisation policy instituted by Bank Indonesia, coupled with maintained foreign capital inflows, primarily to SBN instruments, and the conversion of foreign exchange into rupiah by exporters after the Government strengthened policy concerning the foreign exchange proceeds of exports of natural resources (DHE SDA). Moving forward, Bank Indonesia expects the rupiah to remain stable, underpinned by Bank Indonesia's commitment to maintain rupiah stability, together with attractive yields, low inflation and the positive economic growth outlook for Indonesia. Furthermore, Bank Indonesia continues strengthening its stabilisation policy response, including measured intervention in offshore NDF markets and triple intervention strategy with a focus on spot and DNDF transactions, while also purchasing SBN in the secondary market. Bank Indonesia also continues optimising the full panoply of monetary instruments available, which includes strengthening its pro-market monetary operations strategy through the SRBI, Bank Indonesia Foreign Exchange Securities (SVBI) and Bank Indonesia Foreign Exchange Sukuk (SUVBI) instruments, to boost policy effectiveness in terms of attracting portfolio inflows and supporting rupiah exchange rate stability.
Low Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation was maintained in June 2025, thereby bolstering economic stability. CPI inflation in June 2025 was recorded low at 1.87% (yoy), underpinned by lower core inflation, low volatile food (VF) inflation and manageable administered prices (AP) inflation. Core inflation decreased to 2.37% (yoy) as a result of monetary policy consistency to anchor inflation expectations to the target corridor, accompanied by lower demand. VF inflation remained low at 0.57% (yoy), supported by the adequate supply of key food commodities and close synergy to manage inflation between Bank Indonesia and the Central and Regional Government Inflation Control Teams through the National Movement for Food Inflation Control (GNPIP). Meanwhile, AP inflation remained under control at 1.34% (yoy) despite higher prices of potable water and excise taxes on tobacco products. Looking ahead, Bank Indonesia is confident that CPI inflation will remain under control and within the 2.5%±1% target corridor in 2025 and 2026. Core inflation is projected to remain manageable in line with anchored inflation expectations, adequate economic capacity, managed imported inflation, as well as the positive impact of digitalisation. Bank Indonesia also expects VF inflation to remain manageable, supported by inflation control synergy between Bank Indonesia and the central and regional Government.
Bank Indonesia continues strengthening its monetary policy response to maintain stability and drive economic growth. Bank Indonesia is constantly optimising its monetary operations strategy to strengthen the effective transmission of lower interest rates. In the money market, consistent with the BI-Rate reduction implemented in May 2025 and the monetary operations strategy instituted by Bank Indonesia, the IndONIA money market reference rate also trended downwards to 5.14% on 15th July 2025 from 5.77% prior to the BI-Rate reduction announced in May 2025. Meanwhile, SRBI rates for tenors of 6, 9 and 12 months, as of 11th July 2025, also tracked downward trends, namely from 6.22%, 6.26% and 6.27% before the BI-Rate reduction in May 2025 to 5.85%, 5.86% and 5.87%. On the other hand, SBN yields on tenors of 2 years decreased from 6.13% to 5.86%, while yields on 10-year tenors retreated from 6.71% to 6.56%. In contrast, however, the 1-month term deposit rate increased from 4.81% in May 2025 to 4.85% in June 2025 given competition in the banking industry to secure funding. Lending rates in the banking industry also remain high, namely at 9.16% in June 2025, relatively stable compared with 9.18% in May 2025. Moving forward, Bank Indonesia acknowledges a further opportunity for the banking industry to lower interest rates and increase new loan disbursements to support stronger economic growth.
Bank Indonesia continues optimising its pro-market monetary operations strategy to support adequate liquidity in the money market and banking industry. As of 14th July 2025, the position of SRBI was recorded at Rp782.62 trillion, down from Rp923.53 at the beginning of January 2025, thereby supporting monetary policy to expand liquidity. Meanwhile, the respective positions of SVBI and SUVBI instruments in the same period were recorded at USD3.53 billion and USD491 million. The implementation of Primary Dealers (PD) since May 2024 has also increased SRBI transactions in the secondary market along with repurchase agreement (repo) transactions between market players. In addition, Bank Indonesia is also buying SBN in the secondary market to strengthen monetary policy to expand liquidity, while simultaneously reflecting close synergy with the fiscal policy of the Government. In 2025 (as of 15th July 2025), Bank Indonesia has purchased SBN to the tune of Rp144.90 trillion, through the secondary market totalling Rp102.58 trillion and the primary market totalling Rp42.32 trillion in treasury bills (SPN), including sharia SPN. Moving forward, Bank Indonesia will continue optimising its pro-market monetary operations strategy to maintain adequate liquidity and boost the effectiveness of monetary policy transmission towards achieving the inflation target and maintaining rupiah exchange rate stability.
Loans disbursed by the banking industry must be increased to support economic growth. Credit growth in June 2025 was recorded at 7.77% (yoy), down from 8.43% (yoy) in May 2025. On the supply side, credit growth was influenced by bank prudence when disbursing loans despite faster 6.96% (yoy) growth of third-party funds (TPF). Consequently, the banking industry continued investing in securities and also raised lending standards. On the demand side, the main contributor to credit growth was economic activity, which must be increased. By loan type, growth of investment loans, consumer loans and working capital loans in June 2025 stood at 12.53% (yoy), 8.49% (yoy) and 4.45% (yoy), respectively. By sector, loans disbursed to the trade sector, agriculture and corporate services must be increased to support economic financing. Sharia financing recorded 8.37% (yoy) growth, while MSME loan growth stood at 2.18% (yoy) in the reporting period. Moving forward, Bank Indonesia will continue nurturing bank lending, which includes through accommodative macroprudential policies. In addition, Bank Indonesia will also continue strengthening coordination with the Financial System Stability Committee (KSSK) to drive credit growth and support economic financing. Based on the latest developments and policy direction, Bank Indonesia projects growth of loans disbursed by the banking industry in 2025 in the 8-11% range.
Bank Indonesia will strengthen the implementation of Macroprudential Liquidity Incentive Policy (KLM) to revive bank lending/financing. As of the first week of July 2025, Bank Indonesia disbursed KLM incentives totalling Rp376 trillion, with Rp167.1 trillion allocated to state-owned banks, Rp166.7 trillion to national private commercial banks, Rp36.8 trillion to regional government banks and Rp5.8 trillion to foreign bank branches. By sector, the incentives were primarily disbursed to priority sectors, namely agriculture, real estate, public housing, construction, trade and manufacturing, transportation, storage, tourism and the creative economy, as well as the MSME, ultra micro and green sectors. Moving forward, Bank Indonesia will continue strengthening KLM to revive bank lending/financing by optimising the incentives for sectors with a high contribution to economic growth and job creation in line with the Government's Asta Cita program.
Banking industry resilience remains solid, thereby strengthening financial system stability. Bank capital remains high, accompanied by ample liquidity and low credit risk. The Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR) in May 2025 stood at 25.48%, adequate to absorb risk. Meanwhile, ample liquidity was reflected by a 27.05 % ratio of liquid assets to third-party funds (LA/TPF) in June 2025. This was supported by low non-performing loans (NPL), as a proxy of credit risk, as indicated by NPL ratios of 2.29% (gross) and 0.85% (nett) in May 2025. The latest BI stress tests indicate solid banking industry resilience, supported by maintained corporate repayment capacity and profitability. Moving forward, Bank Indonesia will continue strengthening policy synergy with the KSSK Committee to mitigate various domestic and global economic risks that could potentially disrupt financial system stability.
Digital economic and financial transactions continued growing in the second quarter of 2025, supported by secure, seamless and reliable payment systems. Digital payments[1] in the second quarter of 2025 grew 30.51% (yoy) to reach 11.67 billion transactions, supported by all components. Transaction volume through mobile and internet banking applications grew 32.16% (yoy) and 6.95% (yoy), respectively, including digital payment transaction volume through QRIS, which continued enjoying impressive 148.50% (yoy) growth, supported by increasing numbers of users and merchants. From an infrastructure perspective, the volume of retail transactions processed through BI-FAST grew 42.87% (yoy) to reach 1.12 billion transactions, with a value of Rp2,788.31 trillion in the second quarter of 2025. On the wholesale or high-value side, the BI-RTGS system processed 2.32 million transactions in the second quarter of 2025, with a transaction value of Rp47,481.04 trillion. In terms of rupiah currency management, total currency in circulation grew 9.00% (yoy) to Rp1,153.04 trillion in the second quarter of 2025.
Payment system stability has been maintained, supported by stable infrastructure and a sound industry structure. In terms of the infrastructure, payment system stability is reflected in the seamless and reliable payment systems maintained by Bank Indonesia, along with an adequate money supply of currency fit for circulation in appropriate denominations in the second quarter of 2025. A healthy payments industry structure is reflected by increasing payment system interconnection, accompanied by the continued expansion of the digital economy and finance ecosystem. Payment transactions based on the National Open API Payment Standard (SNAP) continue to grow as SNAP adoption among various industry players expands. Meanwhile, Bank Indonesia will continue ensuring the availability, reliability and security of the retail and wholesale payment systems operated by Bank Indonesia and the industry. Furthermore, Bank Indonesia will safeguard the adequate availability of rupiah currency fit for circulation in suitable amounts throughout all regions of the Republic of Indonesia, particularly in frontier, outermost and remote regions.
Jakarta, 16th July 2025
Communication Department
Ramdan Denny Prakoso
Executive Director
[1] Digital payments include transactions through mobile applications and the internet.