The money market is a component of the financial system that provides short-term trading, lending or funding activities with a maturity of up to one year denominated in rupiah or a foreign currency.
Money Market Regulations comply with prevailing state treasury laws in terms of utilising government debt securities (SUN) as a monetary instrument through monetary operations based on repurchase agreements (repo). Furthermore, Money Market Regulations provide a solid legal foundation for market participants as a reference and a form of legal assurance when transacting in the money market.
Blueprint for Money Market and Foreign Exchange Market Deepening or
Blueprint Pendalaman Pasar Uang dan Pasar Valuta Asing (BPPU) 2030 is a comprehensive roadmap to navigate the direction of deepening modern and deep money market and foreign exchange markets during the 2025-2030 period.

The Blueprint for Money Market and Foreign Exchange Market Deepening or
Blueprint Pendalaman Pasar Uang dan Pasar Valuta Asing (BPPU) 2030 strengthens the previous BPPU 2025 to support monetary policy transmission, financial system stability and national economic financing. BPPU 2030 also represents the implementation of Bank Indonesia's mandate and authority in the money market and foreign exchange market in accordance with Act No. 4 of 2023 concerning Financial Sector Development and Strengthening (PPSK Act).
Deep and efficient money and foreign exchange market will support development of the other financial market segment such as government securities (SBN) market. In addition, deep and efficient money and foreign exchange markets will enable banks, market players or corporations to manage liquidity and hedge against exchange rate and interest rate risks thereby, supporting economic financing.
The strategies for deepening money market and foreign exchange market, as outlined in the Blueprint for Money Market and Foreign Exchange Market Deepening or
Blueprint Pendalaman Pasar Uang dan Pasar Valuta Asing (BPPU) 2030, are as follows:
- Product and pricing development,
- Market participant and infrastructure development, and
- Synergy and coordination, with pro-market monetary operation and surveillance, digitalisation and economic financing strategy.
The strategic targets of money market and foreign exchange market deepening are as follows:
- Liquid money market and foreign exchange market transction,
- Stability of market and infrastructure,
- Efficient pricing aligned with market conduct.
For more information, download The Blueprint for Money Market and Foreign Exchange Market Deepening (BPPU) 2030.
Download BPPU 2030 (in Bahasa)
For more information, download The Blueprint for Money Market and Foreign Exchange Market Development (BPPU) 2025.
Download BPPU 2025
A Money Market and Foreign Exchange Market Primary Dealer (PUVA Primary Dealer) is a bank and/or other institution approved by Bank Indonesia to fulfill specific obligations and conduct designated activities in the money market and foreign exchange market. Strengthening the role of primary dealers is essential to support monetary transmission through the implementation of the Monetary Operations (MO) strategy and the development of modern and advanced money and foreign exchange markets
Provisions regarding PUVA PD are stipulated in Bank Indonesia Regulation (PBI) Number 6 of 2024 concerning the Money Market and Foreign Exchange Market and the Board of Governors Regulation (PADG) Number 23 of 2024 concerning PUVA Primary Dealers.
Criteria of PUVA Primary Dealers
-
General Criteria:
-
Size,
the scale of financial services provided by the prospective PUVA
Primary Dealers within the financial system and real sector,
-
Interconnectedness,
the degree of linkages of the PUVA
Primary Dealers with the financial system, and
-
Complexity,
includes the substitutability of the PUVA
Primary Dealers within the financial market.
-
Specific Criteria:
-
Transactions,
measured by transactions with Bank Indonesia, the real sector, and cross-border transactions,
-
Interconnection,
evaluated through connections with Bank Indonesia, the real sector, and cross-border linkages,
-
Competence,
based on compliance with human resource competency requirements,
-
Risk Management,
assessed across market, liquidity, and/or operational risk management, and
-
Infrastructure,
evaluated based on technological infrastructure and cybersecurity resilience related to the Money and Foreign Exchange Market..
Bank Indonesia may adjust the criteria and will notify stakeholders via official letter, the Bank Indonesia website, and/or other media.
Obligations PUVA Primary Dealers
PUVA Primary Dealers must:
-
Act as market makers;
-
Actively participate in Bank Indonesia’s Open Market Operations (OMO);
-
Actively engage in money and foreign exchange markets transactions; and
-
Fulfill other obligations in the Money and Foreign Exchange Markets stipulated by Bank Indonesia.
Market making obligation shall be carried out by submitting 2-way price quotations (ask/bid) for repo transactions and SRBI transactions in the secondary market on a daily basis in accordance with the following provisions:
-
Repo Quotations:
-
Submitted daily (business day) from 09:00 to 14:00 WIB;
-
Tenors: overnight (O/N), 1 (one) week, 1 (one) month;
-
Maximum bid-ask spread: 5bps (O/N), 10bps (1 week), and 20bps (1 month);
-
Quotations must be hittable in accordance with each primary dealers' market conduct;
-
Submitted to the Money Market Price Information Platform Provider.
-
SRBI Secondary Market Quotations:
-
Submitted daily (business day) from 09:00 to 14:00 WIB;
-
Minimum of 1 (one) SRBI series owned that is available for transaction;
-
Maximum spread is 20bps;
-
Submitted to the Money Market Price Information Platform Provider.
-
OIS Quotations (non-window matchmaking) :
-
Conducted on every business day;
-
Tenors: 3 (three) months and 12 (twelve) months;
-
Maximum spread: 20 bps for both tenors;
-
Indicative quotations permitted, subject to each Primary Dealer's market conduct.
-
Submitted to the Money Market Price Information Platform Provider.
OMO Participation Obligations
PUVA Primary Dealers must submit bids in Monetary Operation transactions:
-
SRBI auctions: minimum 1 bid per auction day.
-
BI-FRN auctions: minimum 1 bid per auction day.
-
Minimum SRBI winning ratio (over 3 months):
-
KBMI 4: ≥ 3% of total issuance.
-
Other KBMI groups: ≥ 1% of total issuance.
Market Activity Obligations
-
Obligations include:
-
Maintaining counterparty lines with at least 10 PUVA Primary Dealers and 10 non-PUVA Primary Dealers at the end of each period.
-
Achieving a ratio of SRBI secondary-market sell ratio of at least 30% relative to primary-market purchases in each period.
-
Conducting:
-
Repo transactions with a minimum tenor of 2 weeks on at least 60% of business days in each period;
-
SRBI 3-month tenor transaction on at least 60% of business days in each period.
-
Maintaining OIS counterparty lines with at least 10 PUVA Primary Dealers at the end of each period.
-
Participating in OIS Matchmaking for the 1-month and 3-month tenors in accordance Bank Indonesia's Rules of the Game.
Effective Dates:
-
OIS quotations, BI-FRN bid obligations, and OIS Matchmaking: effective
2 January 2026.
-
OIS counterparty-line requirement: evaluated as of
31 March 2026.
Activities Permitted for PUVA Primary Dealers
PUVA Primary Dealers may:
-
Access facilities designated for PUVA PDs,
-
Participate in Bank Indonesia's open market operations (OMO);
-
Receive information relevant to PUVA Primary Dealer roles;
-
Conduct other activities determined by Bank Indonesia as needed.
Bank Indonesia may specify additional activities through official communication.
Facilities for PUVA Primary Dealers
PUVA Primary Dealers may access:
-
Repo facilities, subject to fulfillment of SRBI and repo activity obligations within a period evaluated by Bank Indonesia;
-
DNDF facilities from Bank Indonesia;
Facilities Access Period:Fulfilment of obligations during the evaluation period (16th of the month to 15th of the following month) grants access to facilities in the
subsequent month. For example, fulfil the primary dealer obligations in the period from 16th April 2025 – 15th May 2025 to gain access to the PUVA Primary Dealers repo facility in June 2025, and in the period from 16th May 2025 – 15th June 2025 to gain access to the PUVA Primary Dealers repo facility in July 2025 and so on.
Bank Indonesia's Monetary Operation with PUVA Primary DealersPUVA Primary Dealers participate in:
-
SRBI auctions;
-
BI-FRN auctions;
-
Conventional rupiah repo auctions using corporate bonds and sukuk as underlying instruments.
Reporting Requirements
PUVA Primary Dealers must submit and/or provide data, information, reports, descriptions, and/or explanations concerning activities in the money market and foreign exchange market and/or business activities relating to Bank Indonesia. The types of reports include:
-
Transactional Reports via the Integrated Commercial Bank Report (LBUT) through ANTASENA, in accordance with existing reporting obligations. The reports may be used for evaluating PUVA Primary Dealers.
-
Additional Reports requested by Bank Indonesia, including work plans and annual reports, used to monitor fulfilment of special criteria and action plans.
Primary Dealers are required to submit their work plans for the 2026 period before 31 January 2026. The submission should be submitted to Bank Indonesia via electronic mail addressed to komunikasi_du@bi.go.id.
The guideline and submission format are available in the attachment:
The guideline and submission format
Consultation and Licensing
Bank Indonesia may hold consultations concerning PUVA Primary Dealers in certain periods. Consultations on PUVA Primary Dealers may be requested during designated periods via letter addressed to:
Bank Indonesia c.q. Departemen Pengembangan Pasar Keuangan
Jalan M.H. Thamrin No.2, Jakarta 10350
in softcopy format via email to:
dealerutama@bi.go.id.
Application submitted by prospective PUVA Promary Dealer requirements include:
-
An application letter signed by at least 1 (one) board member
-
Proof or membership in a money market and foreign exchange market self-regulatory organisation (SRO); and
-
A statement confirming the absence of sanctions by relevant authorities.
The format of the application letter and supporting documents to become PUVA Primary Dealers is as follows:
Attachment of the Board of Governors Regulation (PADG)
Applications must be submitted electronically via Bank Indonesia licensing application (https://ease.bi.go.id/) on 26-28 November 2025.
Bank Indonesia conducts periodic supervision and evaluations based on:
-
Quarterly fulfilment of obligations; and
-
Semiannual performance evaluation against general and specific criteria.
Obligation Fulfilment Periods:
-
Period 1: January – March
-
Period 2: April – June
-
Period 3: July – September
-
Period 4: October – December
Performance Evaluation Periods:
-
Period 1: January – June
-
Period 2: July – December
List of PUVA Primary Dealers
The list of institutions designated as PUVA Primary Dealers is available on the Bank Indonesia website via the following link:
List of Primary Dealers
Financial market development must be balanced with the establishment of credible financial markets through efforts to increase market participant competency and integrity. Competency and integrity can be increased by requiring Market Participants ensure their Directors and Employees are credentialled with treasury certification commensurate with the respective market activity and position, while ensuring implementation of the Market Code of Conduct and membership of a treasury professional association.
Efforts to increase the competency and integrity of Market Participants also require the support of trusted Professional Certification Institutions. Professional Certification Institutions must apply good governance in accordance with prevailing professional standards in Indonesia, managed by quality human resources with credible experience and adequate organisational tools.
Bank Indonesia Regulation (PBI) No. 19/5/PBI/2017 concerning Treasury Certification and Market Code of Conduct as well as Board of Governors Regulation (PADG) No. 19/5/PADG/2017 concerning Treasury Certification and Market Code of Conduct provide clarity concerning market code of conduct mechanisms, membership of treasury professional associations, treasury certification commensurate with market activity and position, the criteria of Professional Certification Institutions recognised by Bank Indonesia, as well as reporting obligations by Market Participants and Professional Certification Institutions.
The main provisions of the regulations are recapitulated as follows:
- The Market Code of Conduct are guidelines for Directors and Employees of Market Participants referring to the codes of ethics published by conventional and Islamic associations/committees in the financial services industry. The code of ethics must be understood and applied by all Directors and Employees of Market Participants, which are required to maintain internal procedures that contain the Market Code of Conduct.
- Market participants are required to ensure their Directors and Employees are members of professional associations in accordance with conventional or Islamic principles.
- The regulations stipulate the validity period, extensions, positions and maintenance of treasury certification.
- The regulations and provisions concerning organisational tools, certification schemes and administration of treasury certification by professional certification institutions recognised by Bank Indonesia.
- Reporting requirements for Market Participants and Professional Certification Institutions to Bank Indonesia.
- Sanctions and penalties for Market Participants and Professional Certification Institutions.
The Market Code of Conduct represents the professional ethical norms that must be maintained or avoided as behavioural guidelines for the Money Market and Foreign Exchange Market.
To strengthen financial market credibility by increasing market participant competence and integrity, Bank Indonesia issued Bank Indonesia Regulation (PBI) No. 19/5/PBI/2017 concerning Treasury Certification and Market Code of Conduct as well as Board of Governors Regulation (PADG) No. 19/5/PADG/2017 concerning Treasury Certification and Market Code of Conduct, as amended by Board of Governors Regulation (PADG) No. 21/21/PADG/2019. The regulations were issued to instil a code of conduct in Indonesia.
Statement of Commitment to Market Codes
As stipulated in prevailing regulations, a Statement of Commitment to Market Codes is a form of commitment by Market Participants to implement the Market Code of Conduct. Market Participants can submit to Bank Indonesia a Statement of Commitment based on the results of internal self-assessment for publication. The Statement of Commitment is a form of institutional commitment to consistently implement the Market Code of Conduct in terms of treasury activities.
By adopting the Market Code of Conduct, Market Participants receive the following benefits:
- Broader implementation of the market code of conduct in treasury activities in accordance with international best market practices.
- Informing stakeholders as well as domestic and international investors that the institution is committed to implementing the market code of conduct, from which the stakeholders will receive positive benefits.
- Providing competitive advantage for Market Participants regarding effectiveness and behaviour when transacting.
- Supporting implementation of financial market development policies in Indonesia through efforts to create transparent, effective and resilient financial markets.
Disclaimer
The Statement of Commitment is a form of institutional commitment to consistently implement the Market Code of Conduct in terms of treasury activities and, as such, Bank Indonesia bears no responsibility for the Statement of Commitment.
| 1 |
PT. Bank Artos Indonesia |
7 Jan 2020
|
2 Jan 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001B1001 |
| 2 |
PT. Bank Multiarta Sentosa |
21 Jan 2022
|
14 Jan 2022
|
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2201B2002
|
| 3 |
PT. BPD Papua |
21 Jan 2022
|
21 Jan 2022
|
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2201B2004
|
| 4 |
PT. Bank Panin Dubai Syariah, Tbk |
10 Jan 2020 |
8 Jan 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001B2005 |
| 5 |
PT Bank BTPN Tbk |
21 Feb 2024
|
3 Jan 2024
|
Bank
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2402K30126
|
| 6 |
PT. Bank CIMB Niaga, Tbk |
14 Jan 2020 |
27 Jan 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001B4007 |
| 7 |
PT. Mandiri Sekuritas |
14 Jan 2020 |
13 Jan 2020 |
Securities Company
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001S6008 |
| 8 |
PT. BPD Kalimantan Selatan |
15 Jan 2020 |
7 Jan 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001B2009 |
| 9 |
PT. BPD Kalimantan Selatan Shariah Business Unit |
15 Jan 2020 |
7 Jan 2020 |
Shariah Business Unit |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001U5010 |
| 10 |
PT. Bank Nationalnobu, Tbk |
17 Jan 2020 |
29 Nov 2019 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001B2011 |
| 11 |
PT. BPD Jawa Barat dan Banten, Tbk |
20 Jan 2020 |
31 Dec 2019 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001B3012 |
| 12 |
PT. BPD Jawa Tengah Shariah Business Unit |
20 Jan 2020 |
16 Jan 2020 |
Shariah Business Unit |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001U5013 |
| 13 |
PT. Bank Ganesha |
21 Jan 2020 |
16 Jan 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001B2014 |
| 14 |
PT. Bank Aceh Syariah |
12 Jan 2024
|
4 Jan 2024
|
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2401K10120
|
| 15 |
PT. Bank ANZ Indonesia |
23 Jan 2020 |
23 Jan 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001B3016 |
| 16 |
PT. Bank Commonwealth |
24 Jan 2020 |
27 Dec 2019 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001B2017 |
| 17 |
PT. BPD DKI |
27 Jan 2020 |
23 Jan 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001B3018 |
| 18 |
PT. Bank SBI Indonesia |
11 Jan 2024
|
9 Jan 2024
|
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2401K10119
|
| 19 |
PT. Bank Woori Saudara Indonesia 1906, Tbk |
29 Jan 2020 |
27 Jan 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001B2020 |
| 20 |
PT. Bank Amar Indonesia |
30 Jan 2020 |
13 Dec 2019 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001B2021 |
| 21 |
PT. BPD Maluku dan Maluku Utara |
30 Jan 2020 |
22 Jan 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001B2022 |
| 22 |
PT. Bank Victoria Syariah |
30 Jan 2020 |
29 Jan 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001B1023 |
| 23 |
PT. Bank OCBC NISP, Tbk |
31 Jan 2020 |
29 Jan 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001B3024 |
| 24 |
PT. Bank Permata, Tbk |
11 Jan 2024
|
10 Jan 2024
|
Bank
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2401K30118
|
| 25 |
PT. Prima Master Bank |
31 Jan 2020 |
2 Jan 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001B1026 |
| 26 |
PT. BPD Kalimantan Tengah |
31 Jan 2024
|
22 Jan 2024
|
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2401K10121
|
| 27 |
PT. Bank OCBC NISP, Tbk Shariah Business Unit |
31 Jan 2020 |
29 Jan 2020 |
Shariah Business Unit |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2001U5028 |
| 28 |
PT. Bank Permata, Tbk Shariah Business Unit |
18 Mar 2024
|
11 Jan 2024
|
Shariah Business Unit |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2403U50128 |
| 29 |
PT. Bank Harda Internasional |
18 Feb 2020 |
10 Feb 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2002B1030 |
| 30 |
PT. Bank IBK Indonesia, Tbk |
26 Feb 2020
|
13 Feb 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2002B1031 |
| 31 |
PT. BPD Bengkulu |
21 Feb 2020
|
13 Feb 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2002B1032 |
| 32 |
PT. Bank MNC Internasional, Tbk |
5 Mar 2020 |
18 Feb 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2003B2033 |
| 33 |
JP Morgan Chase Bank, NA. |
12 Mar 2020
|
12 Mar 2020
|
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2003B2034 |
| 34 |
PT. Bank Net Indonesia Syariah |
20 Mar 2020 |
20 Mar 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2003B1035 |
| 35 |
PT Bank Mega Tbk |
19 Dec 2023
|
19 Dec 2023
|
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-23012K30116
|
| 36 |
PT. Bank Mandiri Taspen |
1 Apr 2020 |
1 Apr 2020
|
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2037 |
| 37 |
PT. BPD Sumatera Selatan dan Bangka Belitung Shariah Business Unit
|
6 Jan 2022
|
5 Jan 2022
|
Shariah Business Unit |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2201U5038
|
| 38 |
Citibank NA |
8 Apr 2020 |
15 Jan 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B3039 |
39
|
PT. Bank Bumi Arta, Tbk |
9 Apr 2020 |
8 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2041 |
40
|
PT. Bank Capital Indonesia, Tbk |
13 Apr 2020 |
13 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2042 |
41
|
PT. Bank Central Asia, Tbk |
13 Apr 2020 |
14 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B4043 |
42
|
PT. Bank China Construction Bank Indonesia Tbk. |
23 Mar 2020 |
13 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2003B2044 |
43
|
PT. Bank HSBC Indonesia |
13 Apr 2020 |
8 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B3045 |
44
|
PT. Bank ICBC Indonesia
|
6 Apr 2023
|
24 Mar 2023
|
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2304B30110
|
45
|
PT. Bank Index Selindo |
13 Apr 2020 |
13 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2047 |
46
|
PT. Bank Jasa Jakarta |
9 Apr 2020 |
7 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2048 |
47
|
PT. Bank JTrust Indonesia, Tbk |
14 Apr 2020 |
8 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2049 |
48
|
PT. Bank KEB Hana Indonesia |
13 Apr 2020 |
7 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B3050 |
49
|
PT. Bank Maybank Indonesia, Tbk |
19 Apr 2020 |
16 Mar 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2003B3051 |
50
|
PT. Bank Mayora |
9 Apr 2020 |
13 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2052 |
51
|
PT Bank Mestika Dharma
|
14 Mar 2024
|
7 Mar 2024
|
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2403K10127
|
52
|
PT. Bank Mizuho Indonesia |
1 Apr 2020 |
1 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B3054 |
53
|
PT. Bank Negara Indonesia (Persero), Tbk |
8 Apr 2020 |
9 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B4055 |
54
|
PT. Bank Victoria International, Tbk |
14 Apr 2020 |
7 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2056 |
55
|
Standard Chartered Bank |
13 Apr 2020 |
7 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B3057 |
56
|
PT. BPD Jambi |
8 Apr 2020 |
30 Mar 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2058 |
57
|
PT. BPD Kalimantan Barat |
9 Apr 2020 |
13 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2059 |
58
|
PT. BPD Lampung |
14 Apr 2020 |
9 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B1060 |
59
|
PT. BPD Nusa Tenggara Timur |
13 Apr 2020 |
7 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2061 |
60
|
PT. BPD Sulawesi Selatan dan Sulawesi Barat |
7 Apr 2020 |
7 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2062 |
61
|
PT. BPD Sumatera Selatan dan Bangka Belitung |
9 Apr 2020 |
28 Feb 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2063 |
62
|
PT. Bank BRI Syariah, Tbk |
14 Apr 2020 |
13 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2064 |
63
|
PT. Bank Muamalat Indonesia, Tbk |
13 Apr 2020 |
13 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2065 |
64
|
PT. Bank Jabar Banten Syariah |
8 Apr 2020 |
9 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B1066 |
65
|
PT. BPD Jambi Shariah Business Unit |
9 Apr 2020 |
30 Mar 2020
|
Shariah Business Unit |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004U5067 |
66
|
PT. Bank Bisnis Internasional |
13 Apr 2020 |
13 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B1068 |
67
|
PT. Bank CTBC Indonesia |
14 Apr 2020 |
13 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2069 |
68
|
PT. Bank Kesejahteraan Ekonomi |
15 Apr 2020 |
14 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B1070 |
69
|
PT. Bank Mandiri (Persero), Tbk |
13 Apr 2020 |
23 Mar 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B4071 |
70
|
PT. Bank of India Indonesia, Tbk |
13 Apr 2020 |
8 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2072 |
71
|
PT. Bank Sinarmas, Tbk |
14 Apr 2020 |
13 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2073 |
72
|
PT. BPD Daerah Istimewa Yogyakarta |
13 Apr 2020 |
9 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2074 |
73
|
PT. Bank BCA Syariah |
13 Apr 2020 |
13 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B2075 |
74
|
PT. Bank Danamon Indonesia |
20 Apr 2020 |
15 Apr 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004B3076 |
75
|
PT. BPD Riau dan Kepulauan Riau Shariah Business Unit |
22 Apr 2020 |
13 Apr 2020 |
Shariah Business Unit |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2004U5077 |
76
|
PT. BPD Sumatera Barat |
21 Oct2020 |
19 Oct2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2010B2078 |
77
|
PT. Bank Shinhan Indonesia
|
1 Aug 2022 |
15 Feb 2022
|
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2012B2079
|
78
|
PT. Bank UOB Indonesia |
7 Jan 2021 |
5 Jan 2021 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2101B3080 |
| 79 |
PT. BPD Bali |
22 Dec 2020 |
6 Mar 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2012B2081 |
80
|
PT. BPD Kalimantan Timur dan Kalimantan Utara |
30 Dec 2020 |
30 Dec 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2012B2082 |
81
|
PT. BPD Sumatera Utara |
4 Jan 2021 |
30 Dec 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2101B2083 |
82
|
PT. Bank BNI Syariah |
18 Dec 2020 |
17 Dec 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2012B2084 |
83
|
PT. BPD Kalimantan Timur dan Kalimantan Utara Shariah Business Unit |
30 Dec 2020 |
23 Dec 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2012U5085 |
84
|
PT. Amstel Indonesia |
21 Dec 2020 |
18 Dec 2020 |
Money Broker |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2012P7086 |
85
|
PT. Emco Transforex Internasional |
23 Dec 2020 |
18 Dec 2020 |
Money Broker |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2012P7087 |
| 86 |
PT. Global Sarana Lintas Artha |
21 Dec 2020 |
18 Dec 2020 |
Money Broker |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2012P7088 |
87
|
PT. Nusantara Mahabakti |
21 Dec 2020 |
17 Dec 2020 |
Money Broker |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2012P7089 |
88
|
PT. Tradition Indonesia |
21 Dec 2020 |
17 Dec 2020 |
Money Broker |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2012P7090 |
89
|
PT. BPD DKI Shariah Business Unit |
30 Dec 2020 |
30 Dec 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2012U5091 |
| 90 |
PT. Bank Digital BCA |
30 Dec 2020 |
17 Dec 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2012B1092 |
91
|
PT. BPD Sulawesi Selatan dan Sulawesi Barat Shariah Business Unit |
31 Dec 2020 |
29 Dec 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2012U5093 |
92
|
PT. Bank Tabungan Negara (Persero), Tbk Shariah Business Unit |
30 Dec 2020 |
29 Dec 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2012U5094 |
93
|
PT. Bank Syariah Mandiri |
30 Dec 2020 |
28 Dec 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2012B3095 |
94
|
PT. BPD Kalimantan Barat Shariah Business Unit |
23 Dec 2020 |
22 Dec 2020 |
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2012U5096 |
95
|
PT. Bank Artha Graha Internasional, Tbk
|
4 Mar 2021
|
4 Mar 2021
|
Bank
|
 Unduh.pdf Unduh.pdf
|
R-2103B2097
|
96
|
PT. Bank Nagari Shariah Business Unit
|
4 Apr 2022
|
4 Apr 2022
|
Shariah Business Unit
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2204U5098
|
97
|
Bank Of China (Hong Kong) Limited Jakarta Branch |
22 Jul 2022
|
22 Jul 2022
|
Bank
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2207B2099
|
98
|
PT Bank Maspion Indonesia Tbk
|
23 Nov 2023
|
24 Oct 2023
|
Bank
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-23011K10114
|
99
|
MUFG BANK, Ltd
|
8 Sep 2022
|
1 Sep 2022
|
Bank
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2209B3101
|
100
|
PT. Bank CTBC Indonesia |
13 Sep 2022
|
13 Sep 2022
|
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf |
R-2209B2102 |
101
|
PT. Bank BTPN Syariah, Tbk
|
20 Sep 2022
|
30 Aug 2022 |
Bank
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2209B3103 |
102
|
PT. Pilar Dana
|
8 Jan 2024
|
8 Jan 2024
|
Money Broker
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2401P70117
|
103
|
PT. BPD Jawa Timur, Tbk
|
16 Jan 2023
|
12 Jan 2023
|
Bank
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2301B3105
|
104
|
PT. Bank Fama International
|
18 Jan 2023
|
18 Jan 2023
|
Bank
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2301B1106
|
105
|
PT Bank Sahabat Sampoerna
|
5 Dec 2023
|
1 Dec 2023
|
Bank
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-23012K10115
|
106
|
PT. Bank Permata, Tbk |
28 Mar 2023
|
13 Mar 2023
|
Bank
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2303B30109
|
107
|
PT. BPD Sulawesi Tenggara, Tbk
|
4 Apr 2023
|
28 Mar 2023
|
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2304B10111
|
108
|
PT. Bank Nationalnobu, Tbk
|
11 Apr 2023
|
3 Mar 2023
|
Bank |
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2304B2011
|
109
|
PT. Bank Jago, Tbk |
21 Jun 2023
|
19 Jun 2023
|
Bank
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2306B3001
|
110
|
PT. Bank Resona Perdania
|
2 Aug 2023
|
13 Jul 2023
|
Bank
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2308K10112
|
111
|
Bank of America, N.A. |
5 Feb 2024
|
5 Feb 2024
|
Bank
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2402K10122
|
112
|
PT Bank QNB Indonesia Tbk
|
22 Jan 2024
|
18 Jan 2024
|
Bank
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2401K10123
|
113
|
PT Bank BNP Paribas Indonesia
|
27 Jan 2021
|
6 Jan 2021 |
Bank
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2101K20124
|
114
|
PT BPD Jawa Timur Tbk (Shariah Business Unit)
|
7 Mar 2024
|
19 Feb 2024
|
Shariah Business Unit
|
 Download.pdf Download.pdf
|
R-2403U50125
|
Market development can be achieved through the advancement of money market instruments in order to expand the variety of instruments available to market participants. Certificates of Deposit (CD) are an alternative money market instrument recently developed.
In March 2017, Bank Indonesia issued Bank Indonesia Regulation (PBI) No. 19/2/PBI/2017 concerning Certificate of Deposit (CD) Transactions in the Money Market. As the money market authority, Bank Indonesia regulates, licences, develops and supervises money market instruments, including certificates of deposit (CD), transacted in the money market. Furthermore, the Bank Indonesia regulation provides a solid legal foundation for market participants to transact with certificates of deposit (CD) in the money market.
In terms of regulatory implementation, Bank Indonesia issued implementation guidelines in the form of a Board of Governors regulation for issuers and market participants transacting with certificates of deposit (CD) in the money market, covering aspects of licensing, reporting and supervision.
The salient provisions of the regulation are as follows:
- Licence application procedures for Banks, Securities Companies and Brokers:
-
Licence application processing:
-
Bank Indonesia will grant or reject a licence application in writing within 10 working days upon receipt of a complete application and supporting documentation in line with prevailing regulations.
-
Bank Indonesia will conduct administrative verification of the documentation submitted in accordance with the Bank Indonesia regulation concerning Certificate of Deposit (CD) Transactions in the Money Market and implementation guidelines.
-
Bank Indonesia will conduct further clarification in the form of:
-
Based on the results of the administrative verification, Bank Indonesia will decide to:
-
Information Disclosure
Banks issuing Certificates of Deposit (CD) to be transacted in the Money Market must declare “transactable in the money market” on the front page of the prospectus offered to investors.
-
Reporting
-
Banks, Securities Companies and Brokers must report to Bank Indonesia as follows:
- Certificate of Deposit Transaction Report submitted by a Bank or Securities Company on behalf of itself.
- Certificate of Deposit Transaction Report submitted by a Securities Company or Broker as intermediary on behalf of a customer.
-
Reports must be submitted to Bank Indonesia through the following mechanisms:
-
Supervision
-
Bank Indonesia conducts supervision of Banks, Securities Companies, Brokers as well as Depository and Settlement Institutions in relation to issuances and transactions of certificates of deposit (CD) in the Money Market.
-
Supervision includes:
Money Market development requires the development of money market instruments, including Commercial Securities.
Commercial securities are money market instruments issued by non-bank corporations with a maturity of up to one year as an alternative form of short-term funding or liquidity management available to non-bank corporations. Meanwhile, the development of commercial securities as a money market instrument will provide greater liquidity management flexibility for Market Participants.
Bank Indonesia is authorised to regulate short-term money market instruments with a maturity period of up to one year in accordance with the provisions stipulated in Article 70 of Law No. 8 of 1994 concerning the Capital Market along with the corresponding elucidation. Article 70 states that Commercial Securities are a money market instrument exempt from public offering obligations considering that the development, regulation and supervision of such securities with a maturity period of up to one year are conducted by a separate institution.
As the money market authority, Bank Indonesia regulates the money market and instruments therein through Bank Indonesia Regulations. In addition, to strengthen money market credibility as a medium of monetary policy transmission in general and the commercial securities market in particular, Bank Indonesia has also regulated commercial securities as a money market instrument in accordance with Bank Indonesia Regulation (PBI) No. 19/9/PBI/2017 concerning Issuances and Transactions of Commercial Securities in the Money Market.
The regulations on commercial securities are focused on creating a qualified investor base. Qualified investors have strong investment knowledge and understand the risks. One way to create a qualified investor base is by enforcing a lower limit on purchases of Commercial Securities at Rp500 million. Consequently, the Bank Indonesia regulation distinguishes between qualified and unqualified investors regarding aspects of information disclosure.
Financial markets play a strategic role in terms of funding economic activity, transmitting monetary and fiscal policies as well as maintaining financial system stability. The research literature shows that deep financial markets can accelerate economic growth. Various breakthroughs to support the financial markets are urgently required to enable infrastructure development as a prerequisite for sustainable economic growth. At least 49.98% of total funds in the financial markets are earmarked to support infrastructure development from 2020-2024.
Moving forward, strategic development initiatives in Indonesia must seek to create deep and globally competitive financial markets, which will provide alternative sources of financing and investment for economic players, while facilitating the risk mitigation needs of market participants and creating transaction efficiency through better quality financial market infrastructure.
Financial market development and deepening can only be accelerated by strengthening coordination between financial market authorities and institutions. Furthermore, the financial market authorities in Indonesia must formulate and agree a national strategy as a reference and form of tangible commitment for all stakeholders. To that and, Bank Indonesia, the Ministry of Finance and the Indonesian Financial Services Authority (OJK) established the Financial Market Development and Deepening Coordination Forum (FK-PPPK).
FK-PPPK is mandated with formulating the National Financial Market Development and Deepening Strategy (SN-PPPK) as a comprehensive and measurable single policy framework oriented towards realising the vision of creating deep, liquid, efficient, inclusive and secure financial markets. Using a top-down approach, therefore, FK-PPPK developed a framework based on three main pillars as follows:
-
Sources of economic financing and risk management.
-
Market infrastructure development.
-
Policy coordination, regulatory harmonisation and education.
The three pillars have been elaborated into development elements for implementation across seven financial markets, namely the government bond market, corporate bond market, money market, foreign exchange market, stock market, structured product market and Islamic financial market.
SN-PPPK implementation has been divided into three stages, namely strengthening the foundations from 2018-2019, the acceleration phrase from 2020-2022 and the deepening phase from 2023-2024.
[download document]
In line with the vision of the National Strategy for Financial Market Development (SN-PPPK) 2018 – 2024, which is to achieve a deep financial market capable of competing globally, the Blueprint for Money Market Development 2025 is present to complement all initiatives and implementation of SN-PPPK consisting of acceleration phase (2020 – 2022) and deepening phase (2023 – 2024) to eventually reach the desired state: a modern and advanced money market in 2025.
The Blueprint for Money Market Development 2025 focuses on three initiatives: 1) promote digitalization and strengthening of financial market infrastructures, 2) strengthen effectiveness of monetary policy transmission, and 3) develop economic financing sources and risk management. These three initiatives are implemented through fourteen key deliverables with various development and strengthening programs related to market products, pricing, and participants, as well as financial market infrastructures. It is expected that this effort will be able to increase market confidence, which may eventually realize a modern and advanced market characterized by a deep, inclusive, and contributive money market environment.
With a deep, inclusive, and contributive market environment, money market will play a significant role to increase effectiveness of monetary policy transmission, thereby supporting monetary stability and financial system stability. It is expected that this condition enables money market as a catalyst to provide financing sources in order to meet the national development requirements. Consequently, money market contributes to the achievement of the vision toward a Developed Indonesia. [download blueprint]
Fair, regulated, transparent, liquid and efficient financial markets with integrity can be realised through reliable and integrated financial market infrastructure.
One form of financial market infrastructure is the means to implement transactions through a platform to set prices and interact with Market Participants as follows:
- Electronic Trading Platform, namely a business entity established specifically to provide certain facilities used to interact and/or transact in the money market and/or foreign exchange market.
- Money Market and Foreign Exchange Market Brokers, namely a business entity established specifically to provide certain transaction facilities for service users and earn a return on the services provided.
- Systematic Internalisers, namely banks that provide certain facilities to perform transactions in the money market and/or foreign exchange market using its own account with Service Users.
- Futures Exchange Providers, namely futures exchanges in accordance with prevailing laws on commodities futures trading, providing specific facilities for service users to transact in the money market and/or foreign exchange market.
Providers of technology and other transaction facilities must comply with good governance and effective risk management procedures in order to create fair, regulated, transparent, liquid and efficient financial markets with integrity. Good governance is achieved through adherence to the market code of conduct, protecting the service users and increasing price transparency.
Transaction facilities have developed rapidly in line with technological advancement. Consequently, various new alternative transaction mechanisms based on electronic systems have emerged for use by Market Participants.
Considering the rapid development of technology in terms of providing novel transaction facilities, coupled with the importance of maintaining good governance as well as encouraging effective risk management, provisions concerning Transaction Service Providers are required in the form of Bank Indonesia Regulations.
-
Timeline
In conjunction with other financial market authorities, Bank Indonesia has communicated the LIBOR transition to all domestic market players. The timeline of the LIBOR transition is as follows:
-
LIBOR Discontinuation Preparedness Survey
a.
Survey of Banking Sector
Bank Indonesia has surveyed the banking sector to identify LIBOR use in the domestic financial markets. The survey revealed LIBOR exposure in the banking industry as well as banking industry preparedness for the discontinuation of LIBOR.
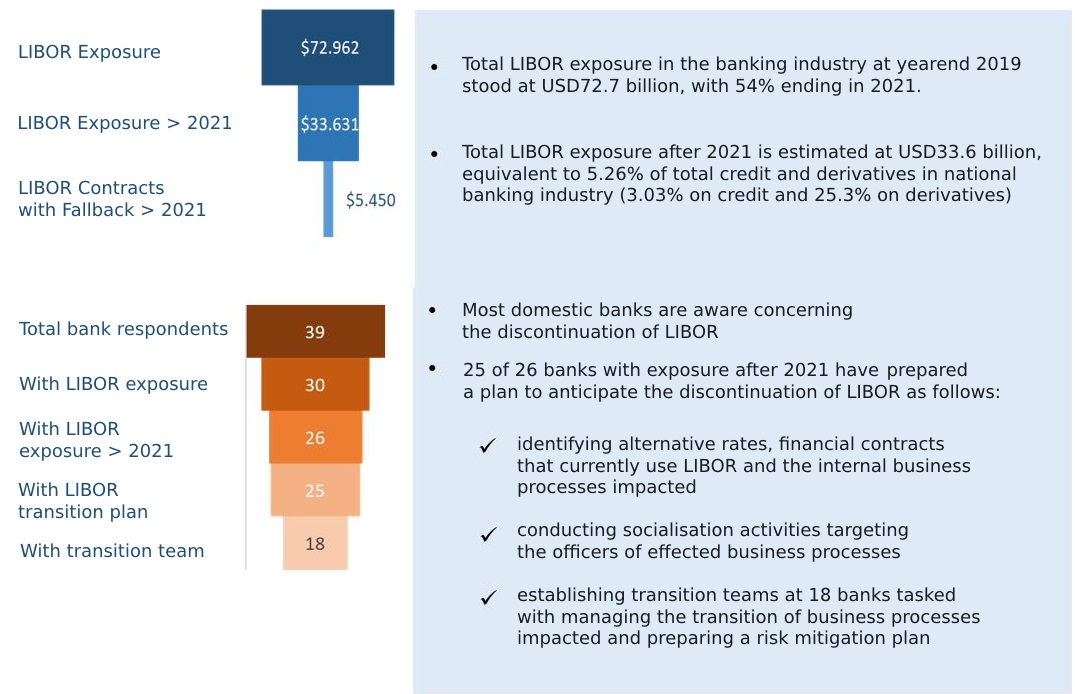
In total, 39 domestic banks actively transacting foreign currencies were surveyed, representing 86% of exposure to foreign currency loans, rupiah loans and foreign currency derivatives. The salient results of the survey are as follows:
b.
Survey of Non-Financial Corporations
At the end of 2020, Bank Indonesia surveyed non-financial corporations with high foreign exchange exposure. With respondents totalling 219 corporations, only 11% or 23 corporations were affected by LIBOR exposure. Of the 23, most (70%) were yet to transition due to insufficient information. Meanwhile, some of the other corporations had identified financial contracts with LIBOR exposure but were yet to transition.
-
CEO Letter
Bank Indonesia has increased the preparedness of market players for the discontinuation of LIBOR by sending a CEO Letter to all banks and several corporations in June 2020. Through the CEO Letter, Bank Indonesia reminded domestic banking industry and corporate sector leaders to undertake the following anticipatory measures:
- Identifying financial contracts using LIBOR
- Preparing contingency plans for the financial contracts using LIBOR through additional fallback clauses with relevant counterparties
- Actively restricting LIBOR use in new financial contracts
- Analysing the actions necessary in the business processes impacted as part of the risk mitigation plan
- Documenting governance of the LIBOR transition
-
National Working Group
In line with FSB-OSSG recommendations and in anticipation of LIBOR discontinuation, Bank Indonesia has coordinated with other domestic financial market authorities, namely the Financial Services Authority (OJK) and Ministry of Finance, as well as engaged in dialogue with industry associations represented by the Indonesia Foreign Exchange Market Committee (IFEMC).
Close coordination and cooperation between domestic financial market authorities represent an important strategic measure to safeguard the massive and measured anticipatory measures required towards LIBOR discontinuation.
In November 2020, the coordination forum agreed to establish a National Working Group to jointly overcome the LIBOR transition challenges, covering legal, accounting, tax, risk management and infrastructure system aspects.
Financial market infrastructures (FMI) refer to all parts of the financial system that facilitate financial market transactions, including settlement. According to IOSCO, an FMI is defined as a multilateral system among participating financial institutions, including the operator of the system, used for the purposes of recording, clearing or settling payments, securities, derivatives or other financial transactions. Several systems are considered systemically important financial market infrastructures based on the criteria set by each respective country. Nevertheless, most definitions refer to post-trade systems.


