Standing Facilities
Standing Facilities are conducted to maintain adequate liquidity for Monetary Operation Participants at the end of the day. Standing Facilities are implemented through the provision and placement of rupiah funds, conducted either conventionally or based on sharia principles.
Standing Facility are available at the end of each day for both conventional and sharia banks, consisting of:
-
Deposit Facility (DF) - the placement of rupiah funds by Standing Facility participants at Bank Indonesia for monetary operations conducted either conventionally or according to sharia principles. DF conducted according to sharia principles is implemented as Bank Indonesia Sharia Deposit Facility (FASBIS).
-
Lending Facility (LF) or Financing Facility (FF) - LF refers to the provision of rupiah funds from Bank Indonesia to conventional Standing Facility participants for monetary operations conducted conventionally, while FF refers to the provision of rupiah funds from Bank Indonesia to sharia Standing Facility participants for monetary operations conducted according to sharia principles.
Standing Facility is implemented through the following instruments:

Foreign Exchange Monetary Operations
Foreign exchange monetary operations (FX MOs) are conducted to manage liquidity and maintain the stability of the rupiah exchange rate. FX MO instruments consist of the issuance of Bank Indonesia securities, repurchase agreements (repos) and/or reverse repos, term deposits at Bank Indonesia, foreign exchange purchase and/or sale transactions, and/or other transactions in the money market and foreign exchange market. FX MOs are conducted with a minimum tenor of 1 (one) day and a maximum tenor of 12 (twelve) months.
FX MOs are conducted through the following instruments:
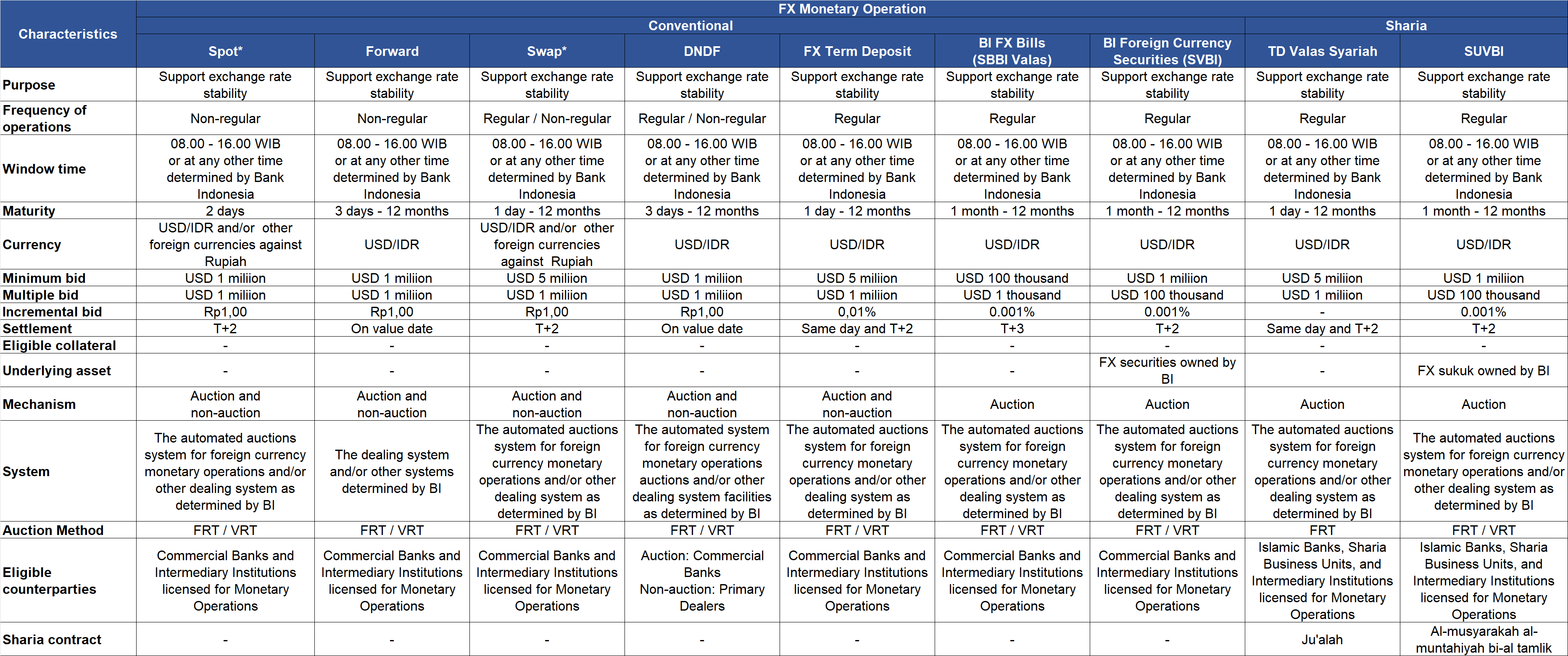
*) Detail Characteristics and auction procedures for spot and swap transactions in other foreign currencies against Rupiah, as attached in
Characteristics and
Auction Procedures
Bank Indonesia announces the schedule and results of rupiah OMO and foreign exchange MO auctions through the BI website and/or other designated media, accessible via the following link:
Monetary Operations Auction Schedule
Monetary Operations Auction Result
Description:
- VRT: Variable Rate Tender
- FRT: Fixed Rate Tender
- SBI: Bank Indonesia Certificate
- SBIS: Sharia Bank Indonesia Certificate
- SDBI: Bank Indonesia Deposit Certificate
- SRBI: Bank Indonesia Rupiah Securities
- BI-FRN: Bank Indonesia Floating Rate Note
- TD: Term Deposit
- SUKBI: Bank Indonesia Sukuk
- FX: Foreign Exchange
- PASBI: Bank Indonesia Sharia-Based Liquidity Facility
- FLISBI: Bank Indonesia Sharia-Based Liquidity Facility
- SBBI: Bank Indonesia Securities
- DNDF: Domestic Non-Deliverable Forward
Related Links:
The weighted average interest rate of MO transaction is the average interest rate of monetary operation transactions that takes into account the winning bid interest rate and weighted by transaction volumes.
More information is accessible via the official
Bank Indonesia website.
Placement of Export Proceeds (DHE SDA) in Foreign Currency Term Deposits (TD Valas) for Foreign Exchange Proceeds of Export (DHE)
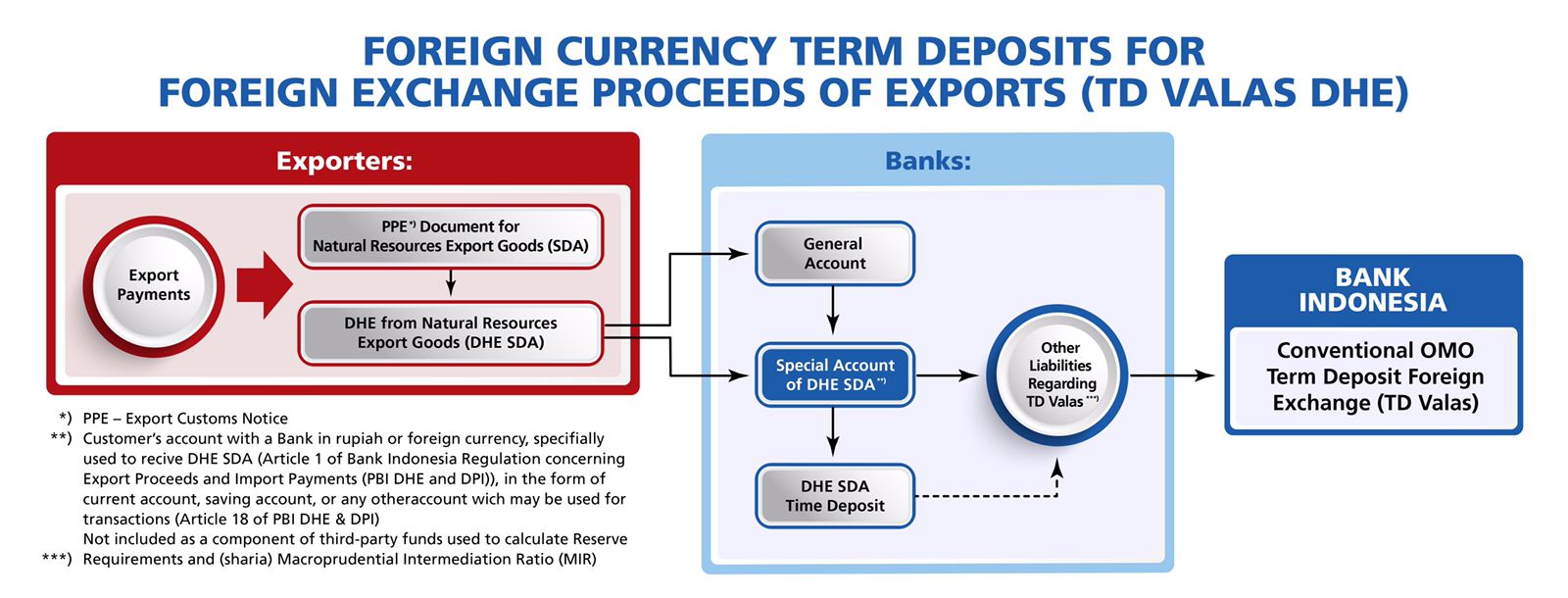
Bank Indonesia has issued a policy to strengthen the management of foreign exchange proceeds of export (DHE) by expanding the transaction mechanisms between Bank Indonesia and banks in the form of a pass on of transactions between banks and their customers (exporters) to Bank Indonesia through Foreign Currency Term Deposits (TD Valas) for Foreign Exchange Proceeds of Export (DHE). Placement of DHE SDA in TD Valas DHE aims to facilitate the DHE placements by exporters at Bank Indonesia through appointed banks in accordance with market mechanisms. To support the policy, Bank Indonesia offers: (i) foreign exchange interest rates taking into account nominal and tenor tiering; (ii) exemption of funds from the third-party funds component used to calculate Reserve Requirements and (sharia) Macroprudential Intermediation Ratio; (iii) agent fees/spread based on tenor for banks taking into account the tenor of TD Valas DHE.
List of Appointed Banks
|
1 |
MUFG Bank, Kantor Cabang Jakarta
|
|
2 |
Citibank N.A., Indonesia
|
|
3 |
JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A
|
|
4 |
PT Bank HSBC Indonesia
|
|
5 |
PT Bank CTBC Indonesia
|
|
6 |
PT Bank KEB Hana Indonesia
|
|
7 |
PT Bank Mega, Tbk
|
|
8 |
PT Bank Mizuho Indonesia
|
|
9 |
PT Bank Multiarta Sentosa, Tbk
|
|
10 |
PT Pan Indonesia Bank, Tbk
|
|
11 |
PT Bank Permata, Tbk
|
|
12 |
Standard Chartered Bank Indonesia
|
|
13 |
PT Bank SMBC Indonesia, Tbk
|
|
14 |
Bank of China (Hong Kong) Limited Jakarta Branch
|
|
15 |
PT Bank Central Asia, Tbk
|
|
16 |
PT Bank CIMB Niaga, Tbk
|
|
17 |
PT Bank Danamon Indonesia, Tbk
|
|
18 |
PT Bank DBS Indonesia
|
|
19 |
PT Bank ICBC Indonesia
|
|
20 |
PT Bank Mandiri (Persero), Tbk
|
|
21 |
PT Bank Maybank Indonesia, Tbk
|
|
22 |
PT Bank Negara Indonesia (Persero), Tbk
|
|
23 |
PT Bank OCBC NISP, Tbk
|
|
24 |
PT Bank Rakyat Indonesia (Persero), Tbk
|
|
25 |
PT Bank UOB Indonesia
|
|
26 |
PT Bank China Construction Bank Indonesia, Tbk
|
27
|
PT Bank Ganesha, Tbk
|
28
|
PT Bank Mayapada Internasional, Tbk
|
29
|
PT Bank QNB Indonesia, Tbk
|
30
|
PT Bank Shinhan Indonesia
|
31
|
PT Bank Tabungan Negara (Persero), Tbk
|
32
|
PT Bank Woori Saudara 1906 Tbk.
|
Note: The list of appointed banks will be reviewed periodically
Placement of DHE SDA in SVBI/SUVBI
In accordance with Bank Indonesia Regulation (PBI) No. 3/2025 concerning the Amendment to Bank Indonesia Regulation (PBI) No. 7/2023 concerning Export Proceeds and Import Payments (PBI DHE & DPI), Bank Indonesia has introduced additional instruments in the form of SVBI and SUVBI in the secondary market as alternative instruments for the placement of export proceeds (DHE SDA). Placements of DHE SDA in SVBI and SUVBI instruments cannot be withdrawn before maturity.
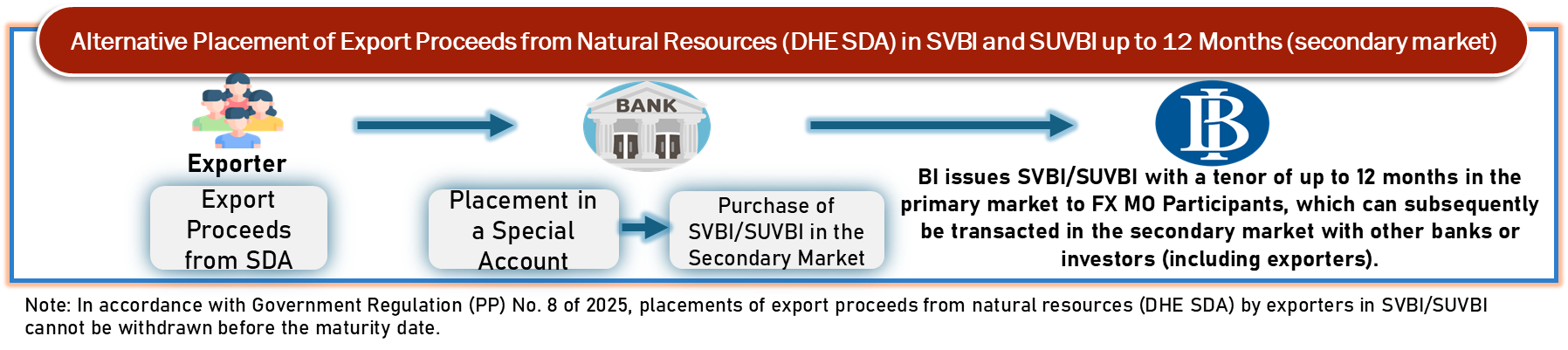
Utilization of TD Valas DHE and SVBI/SUVBI as Underlying Instruments for Hedging Swap Transactions with Bank Indonesia
Placements of export proceeds from natural resources (DHE SDA) in TD Valas DHE instruments as well as in SVBI and SUVBI instruments may be utilized by Banks as underlying instruments for conventional and sharia hedging swap transactions with Bank Indonesia for the benefit of exporters.
A haircut is a deduction factor applied to the price of securities used as collateral in monetary operation to mitigate the market risk among others. The value of haircut applied in monetary operation is evaluated periodically in line with the current condition of securities market and monetary operation.
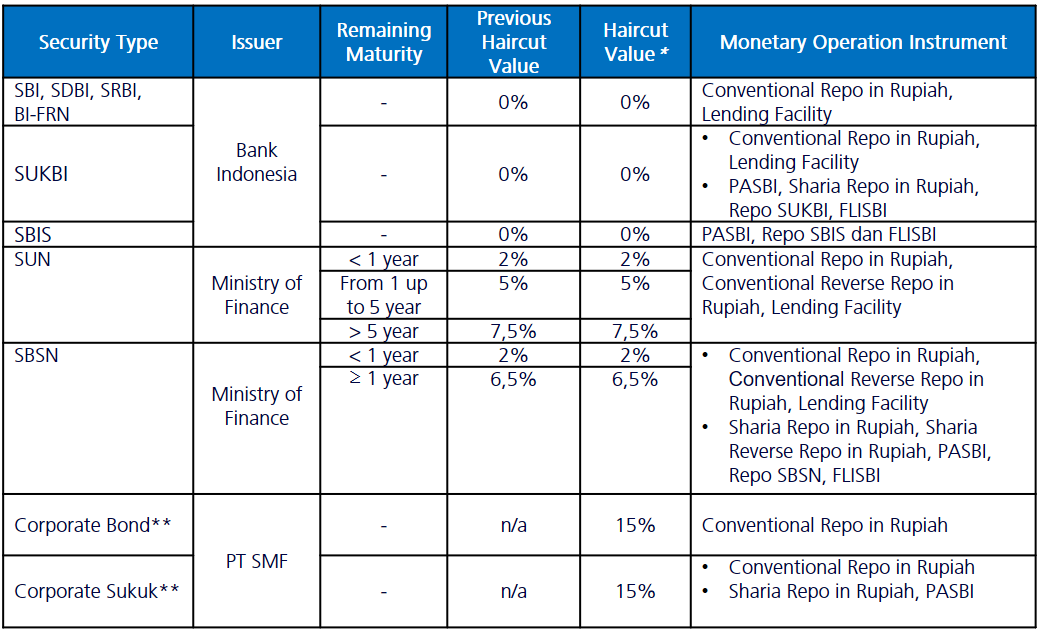
*) Effective from October 20, 2025, as regulated in Regulation of Member of Board of Governors (PADG) No. 18 of 2025 on Criteria, Requirements, and Use of Securities in Monetary Operations.
**) List of corporate bonds and corporate sukuk
as attached.


